1. De viajes, microbios y películas
Tratados
- Naciones Unidas. (1967). Tratado sobre los principios que deben regir las actividades de los Estados en la exploración y utilización del espacio ultraterrestre, incluso la Luna y otros cuerpos celestes. Naciones Unidas. Disponible en: https://www.unoosa.org/oosa/en/ourwork/spacelaw/treaties/outerspacetreaty.html
Libros y relatos
- Campbell Jr., J. W. (1938). ¿Quién anda ahí? Astounding Science Fiction.
- Clarke, A. C. (1944). Los dragones de Titán.
- Clarke, A. C. (1982). 2010: Odisea Dos. Ballantine Books.
- Crichton, M. (1969). The Andromeda Strain. Alfred A. Knopf.
- Lovecraft, H. P. (1927). El color que cayó del cielo. Revista Amazing Stories.
- Wells, H. G. (1898). La guerra de los mundos. William Heinemann Ltd.
Películas
- Espinosa, D. (Director). (2017). Life. Columbia Pictures, Skydance Media.
- Hyams, P. (Director). (1984). 2010: Odisea Dos. Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer.
- Howard, R. (Director). (1995). Apollo 13. Universal Pictures, Imagine Entertainment.
- Scott, R. (Director). (2012). Prometheus. 20th Century Fox, Scott Free Productions.
- Stanley, R. (Director). (2020). El color que cayó del cielo. SpectreVision, ACE Pictures Entertainment, XYZ Films.
- Wise, R. (Director). (1971). La amenaza de Andrómeda. Universal Pictures.
Trabajos científicos
- Arrhenius, S. (1908). Worlds in the Making: The Evolution of the Universe. Harper & Brothers.
- Boothby, T. C., Tapia, H., Brozena, A. H., Piszkiewicz, S., Smith, A. E., Giovannini, I., Rebecchi, L., Pielak, G., Koshland, D., & Goldstein, B. (2017). Tardigrades use intrinsically disordered proteins to survive desiccation. Molecular Cell, 65(6), 975-984.
- Čadek, O., Tobie, G., Van Hoolst, T., Massé, M., Choblet, G., Lefèvre, A., Mitri, G., Baland, R., Běhounková, M., Bourgeois, O., & Trinh, A. (2016). Enceladus’s internal ocean and ice shell constrained from Cassini gravity, shape, and libration data. Geophysical Research Letters, 43(11), 5653-5660.
- Dadachova, E., & Casadevall, A. (2008). Ionizing radiation: How fungi cope, adapt, and exploit with the help of melanin. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 11(6), 525-531.
- Deshevaya, E. A., Shubralova, E. V., Novikova, N. D., & Alekhina, I. A. (2020). Microbiological investigation of the space dust samples collected on the ISS surface. Astrobiology, 20(5), 593-603.
- Rebecchi, L., Altiero, T., Guidetti, R., Cesari, M., Bertolani, R., Negroni, M., & Rizzo, A M. (2009). Tardigrade resistance to space effects: first results of experiments on the LIFE-TARSE on FOTON-M3. Astrobiology, 9(6), 581-591.
- Shmakova, L., Malavin, S., Iakovenko, N., Vishnivetskaya, T., Shain, D., Plewka, M., & Rivkina, E. (2021). A living bdelloid rotifer from 24,000-year-old Arctic permafrost. Current Biology, 31(11), R712-R713.
- Slobodkin, A. I., Gavrilov, S. N., & Chernykh, N. A. (2015). Spore-forming thermophilic bacterium within artificial meteorite survives entry into the Earth’s atmosphere on FOTON-M4 satellite landing module. Plos One, 10(7), e0132611.
- Waite, J. H., Combi, M. R., Ip, W. H., Cravens, T. E., McNutt, R. L., Kasprzak, W., Gell, D., Luhmann, J., Niemann, H., Yelle, R., & Müller-Wodarg, I. (2009). Ion neutral mass spectrometer results from the first flyby of Enceladus: Detection of a dynamic atmosphere. Nature, 460(7254), 487-490.
2. El suelo, un ecosistema a nuestro servicio
- Banerjee S. and van der Heijden M. (2022) Soil microbiomes and one health. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 21: 6-20.
3. El papel de virus y bacterias en los ciclos de nutrientes
- BUCKLEY, D.H.; STAHL, D.A.; MARTINKO, J.M.; et al. (2015) Brock. Biología de los microorganismos. 14ª edición. Pearson.
- CONTRERAS, G.; …; MOLITOR, B. (2022) New perspectives for biotechnological applications of methanogens. Current Research in Biotechnology, 4. pp: 468-474. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crbiot.2022.10.001
- GELDERBLOM, H.R. (1996) Structure and classification of viruses. Capítulo en Medical Microbiology, 4ª edición. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8174
- LARA, E.; VAQUÉ, D.; LAIA SÀ, J.; et al. (2017) Unveiling the role and life strategies of viruses from the surface to the dark ocean. Science Advances, 3(9). DOI: 1126/sciadv.1602565
- MARTÍNEZ-ROMERO, J.; …; MARTÍNEZ-ROMERO, E. (2022) Microbial Symbioses. Reference Module in Life Sciences. Elsevier. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-822563-9.00038-X
- MONTAÑO ARIAS, N.M.; SANDOVAL PÉREZ, A.L.; et al. (2010) Los microorganismos: pequeños gigantes. Elementos: ciencia y cultura, 17(77). pp: 15-23. Disponible en: http://redalyc.uaemex.mx/src/inicio/ArtPdfRed.jsp?iCve=29411989003
4. La biología sintética: Diseñando microorganismos para salvar el planeta
- Arenas, J. M., Carrascal, F., & Montes, C. (2008). Breve historia de la construcción del Corredor Verde del Guadiamar. La restauración ecológica del río Guadiamar y el proyecto del Corredor Verde. La historia de un paisaje emergente, 29-64.
- Domínguez, MT., Madejón, P., Marañón, T. & Murillo, J.M. (2010). Afforestation of a trace-element polluted area in SW Spain: woody plant performance and trace element accumulation. Eur J Forest Rest. 129:47-59.
- Domínguez, MT., Marañón, T. & Murillo, J.M., Schulin, R. & Robinson, BH. (2010). Nutritional status of Mediterranean trees growing in a contaminated and remediated area. Water Air Soil Pollut. 205:305-321.
- Ferreira, P. A. A., Bomfeti, C. A., Soares, C. R. F. D. S., Soares, B. L., & Moreira, F. M. D. S. (2018). Cupriavidus necator strains: zinc and cadmium tolerance and bioaccumulation. Scientia Agricola, 75, 452-460. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-992X-2017-0071
- Franco-Navarro, J.D. (2020). El desastre ambiental del Corredor Verde del Guadiamar. Hidden Nature – Número 11 · 3T/2020 – ISSN 2531-0402. DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.18284.18563. Disponible en el siguiente enlace: https://www.hidden-nature.com/revista/numero-11/el-desastre-ambiental-del-corredor-verde-del-guadiamar/
- Rodríguez, A., Marañón, T., Domínguez, MT., Murillo, J.M., Jordano, D., Fernández Haeger, J. & Carrascal, F. (2009). Reforestación con arbustos para favorecer la conectividad ecológica en El Corredor Verde del Guadiamar. 5º Congreso Forestal Español.
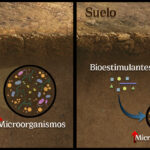
5. Prebióticos y bioestimulantes para la salud del suelo
- Aytenew, M., & Bore, G. (2020). Effects of organic amendments on soil fertility and environmental quality: A review. Plant Sci, 8(5), 112-119.
- Matisic, M., Dugan, I., & Bogunovic, I. (2024). Challenges in Sustainable Agriculture—The Role of Organic Amendments. Agriculture, 14(4), 643.
- Pérez-Burillo, S., Cervera-Mata, A., Fernández-Arteaga, A., Pastoriza, S., Rufián-Henares, J. Á., & Delgado, G. (2022). Why should we be concerned with the use of spent coffee grounds as an organic amendment of soils? A narrative review. Agronomy, 12(11), 2771.
- Roche, D., Rickson, J. R., & Pawlett, M. (2024). Moving towards a mechanistic understanding of biostimulant impacts on soil properties and processes: a semi-systematic review. Frontiers in Agronomy, 6, 1271672.
- Tiwari, J., Ramanathan, A. L., Bauddh, K., & Korstad, J. (2023). Humic substances: Structure, function and benefits for agroecosystems—A review. Pedosphere, 33(2), 237-249.
- Yousfi, S., Marín, J., Parra, L., Lloret, J., & Mauri, P. V. (2021). A rhizogenic biostimulant effect on soil fertility and roots growth of turfgrass. Agronomy, 11(3), 573.
6. Las micorrizas, una solución microbiana para una agricultura y un planeta más sostenibles
- Ahammed, G.J., & Hajiboland, R. (2024). Introduction to Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Higher Plant Symbiosis: Characteristic Features, Functions, and Applications. In: Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Higher Plants (eds. Ahammed, G.J., Hajiboland, R.), pp. 1–17. Springer, Singapore.
- Miyata, K., & Umehara, M. (2024). Roles of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi for Essential Nutrient Acquisition Under Nutrient Deficiency in Plants. In: Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Higher Plants (eds. Ahammed, G.J., Hajiboland, R.), pp. 123–148. Springer, Singapore.
- Parniske, M. (2008). Arbuscular mycorrhiza: the mother of plant root endosymbioses. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 6, 763–775.
- Shi, J., Wang, X., & Wang, E. (2023). Mycorrhizal Symbiosis in Plant Growth and Stress Adaptation: From Genes to Ecosystems. Annual Reviews, 74, 569–607.
- Smith, S. E., & Read, D. J. (2008). Mycorrhizal Symbiosis (3rd ed.). Academic Press. Steinkellner, S., Lendzemo, V., Langer, I., Schweiger, P., Khaosaad, T., Toussaint, J., & Vierheilig, H. (2007). Flavonoids and Strigolactones in Root Exudates as Signals in Symbiotic and Pathogenic Plant-Fungus Interactions. Molecules, 12, 1290–1306.
7. El microbioma ambiental: Clave para alimentos funcionales más sostenibles y saludables.
- Alcázar-Valle, M. et al. Bioactive Compounds, Antioxidant Activity, and Antinutritional Content of Legumes: A Comparison between Four Phaseolus Species. Molecules 25, 3528 (2020).
- Fierer, N. Embracing the unknown: disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol 15, 579–590 (2017).
- Mendes, R., Garbeva, P. & Raaijmakers, J. M. The rhizosphere microbiome: significance of plant beneficial, plant pathogenic, and human pathogenic microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37, 634–663 (2013).
- Singh, B. K., Trivedi, P., Egidi, E., Macdonald, C. A. & Delgado-Baquerizo, M. Crop microbiome and sustainable agriculture. Nat Rev Microbiol 18, 601–602 (2020).
- Yanni, A. E., Iakovidi, S., Vasilikopoulou, E. & Karathanos, V. T. Legumes: A Vehicle for Transition to Sustainability. Nutrients 16, 98 (2024).Zhu, Y.-G. et al. Soil biota, antimicrobial resistance and planetary health. Environment International 131, 105059 (2019).
8. Nematodos: Actores fundamentales en la microbiología del suelo
- Freckman D. Nematodes in Soil Ecosystems. University of Texas Press; 1982. p 1-206.
- Pires D, Vicente CSL, Menéndez E, Faria JMS, Rusinque L, Camacho MJ, Inácio ML. The Fight against Plant-Parasitic Nematodes: Current Status of Bacterial and Fungal Biocontrol Agents. Pathogens. 2022. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11101178.
- Yeates GW, Ferris H, Moens T, van der Putten. The role of nematodes in ecosystems. Nematodes as environmental indicators. Walingford, UK: CAB International. 2009. p. 1-44.
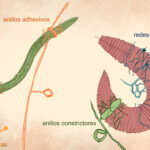
9. Hongos nematófagos: depredadores y aliados
- Al-Ani, L. K. T., De Freitas Soares, F. E., Sharma, A., De los Santos-Villalobos, S., Valdivia-Padilla, A. V., & Aguilar-Marcelino, L. (2022). Strategy of Nematophagous Fungi in Determining the Activity of Plant Parasitic Nematodes and Their Prospective Role in Sustainable Agriculture. Frontiers In Fungal Biology, 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/ffunb.2022.863198
- Jiang, X., Xiang, M., & Liu, X. (2017). Nematode-Trapping Fungi. Microbiology Spectrum, 5(1). https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.funk-0022-2016
- Vidal-Diez de Ulzurrun, G., & Hsueh, Y. (2018). Predator-prey interactions of nematode-trapping fungi and nematodes: both sides of the coin. Applied Microbiology And Biotechnology, 102(9), 3939-3949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8897-5
10. Hongos saprobios: aliados naturales para recuperar la salud de suelos contaminados por metales pesados
- Bareen, F., Shafiq, M., Jamil, S., 2012. Role of plant growth regulators and a saprobic fungus in enhancement of metal phytoextraction potential and stress alleviation in pearl millet. Journal of hazardous materials 237, 186-193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.08.033
- Martín-Peinado, F.J., Romero-Freire, A., García-Fernández, I., Sierra-Aragón, M., Ortiz-Bernad, I., Simón-Torres, M., 2015. Long-term contamination in a recovered area affected by a mining spill. Science of the Total Environment 514, 219-223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.102
- Maurya, G.K., Pachauri, S., 2022. Fungi: The indicators of pollution. In: Bandh, S.A., Shafi, S. (Eds.), Freshwater Mycology, Elsevier, pp. 277-296. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91232-7.00012-X
- Silva-Castro, G.A., Paniagua-López, M., Martín-Peinado, F.J., García-Romera, I., 2021. Hongos saprobios como estrategia de restauración de suelos contaminados por metales pesados. IX Simposio Nacional sobre control de la degradación y recuperación de suelos. http://hdl.handle.net/10261/262772
- Simón, M., García, I., Martín-Peinado, F.J., Díez, M., del Moral, F., Sánchez, J.A., 2008. Remediation measures and displacement of pollutants in soils affected by the spill of a pyrite mine. Science of the Total Environment 407, 23-39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.07.040
- Warnasuriya, S.D., Udayanga, D., Manamgoda, D.S., Biles, C., 2023. Fungi as environmental bioindicators. Science of the Total Environment 892, 164583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164583
- Zhang, M., Zhang, T., Zhou, L., Lou, W., Zeng, W., Liu, T., Yin, H., Liu, H., Liu, X., Mathivanan, K., Praburaman, L., Meng, D., 2022. Soil microbial community assembly model in response to heavy metal pollution. Environmental Research 213, 113576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113576
11. Innovaciones tecnológicas para la detección temprana de microorganismos patógenos cultivos
- Kotwal J, Kashyap R, Pathan S. Agricultural plant diseases identification: From traditional approach to deep learning. Materials Today: Proceedings 2023, 80: 344–356
- Trippa D, Scalenghe R, Basso MF, Panno S, Davino S, Morone C, Giovino A, Oufensou S, Luchi N, Yousefi S, Martinell F. Next-generation methods for early disease detection in crops. Pest Management Science 2024; 80: 245–261. DOI 10.1002/ps.7733
- New method for the detection and identification of pathogens in early stages infections of crops with agro-industrial interest (AgrogenDetect). Programa Estatal para Impulsar la Investigación Científico-Técnica y su Transferencia, del Plan Estatal de Investigación Científica, Técnica y de Innovación 2021-2023, en el marco del Plan de Recuperación, Transformación y Resiliencia. Proyectos de colaboración público-privada 2021. Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovacion. Ref.: CPP2021-008989. Entidades: EEZ-CSIC, CEBAS-CSIC, Microgaia Biotech, SynTech Research Group, Fundación Parque Científico de Madrid, Biotechvana, Paudire R+D+i & Transfer.
12. ¿Es el agua regenerada usada para el riego de vegetales un vector de transmisión de determinantes de resistencia a antimicrobianos?
- COM (2022) 0541, Urban wastewater treatment European Parliament legislative resolution of 10 April 2024 on the proposal for a directive of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning urban wastewater treatment (recast)
- European Commission https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/water/water-scarcity-and-droughts_en (accessed 14/12/2024).
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). (2023). Role of water used in the growing, handling and processing of fruits, vegetables and herbs on the spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) (OC/EFSA/BIOHAW/2023/01).
- Gekenidis MT, Walsh F, Drissner D. Tracing Antibiotic Resistance Genes along the Irrigation Water Chain to Chive: Does Tap or Surface Water Make a Difference? Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Sep 11;10(9):1100. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10091100. PMID: 34572683; PMCID: PMC8469318.
- Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Agencia Estatal de Investigación, & Unión Europea. (2021). Assessment of water disinfection treatments to be used as sustainable wastewater reclamation strategies to mitigate antimicrobial resistance spread through the irrigation of crops RECWATER (TED2021-131427b-C21/C22). Programa NextGenerationEU, Plan de Recuperación, Transformación y Resiliencia.
- Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico (MITECO). (2024). Aprobado el Real Decreto de reutilización de las aguas. Disponible en: miteco.gob.es.
- Oliveira, M., Truchado, P., Cordero-García, R., Gil, M. I., Soler, M. A., Rancaño, A., García, F., Álvarez-Ordóñez, A., & Allende, A. (2023). Surveillance on ESBL-Escherichia coli and Indicator ARG in Wastewater and Reclaimed Water of Four Regions of Spain: Impact of Different Disinfection Treatments. Antibiotics, 12, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030400
13. ¿Seres “invisibles” pueden controlar el cambio climático?
- Cavicchioli, R., Ripple, W.J., Timmis, K.N., Azam, F., Bakken, L.R., Baylis, M., Behrenfeld, M.J., Boetius, A., Boyd, P.W., Classen, A.T., Crowther, T.W., Danovaro, R., Foreman, C.M., Huisman, J., Hutchins, D.A., Jansson, J.K., Karl, D.M., Koskella, B., Mark Welch, D.B., Martiny, J.B.H., Moran, M.A., Orphan, V.J., Reay, D.S., Remais, J.V., Rich, V.I., Singh, B.K., Stein, L.Y., Stewart, F.J., Sullivan, M-B., Van Oppen, M.J.H., Scott C. Weaver, S.C., Webb, E.A., y Nicole S. Webster, N.S. (2019). Scientists’ warning to humanity: microorganisms and climate change. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 17(9), 569-586.
- IPCC, 2023: Sections. In: Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Core Writing Team, H. Lee and J. Romero (eds.)]. IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland, 35-115, doi: 10.59327/IPCC/AR6-9789291691647
- Jiao, N., Luo, T., Chen, Q., Zhao, Z., Xiao, X., Liu, J., Jian, Z., Xie, S., Thomas, H., Herndl, G.J., Benner, R., Gonsior, M., Chen, F., Cai, W., y Robinson, C. (2024). The microbial carbon pump and climate change. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 22, 408-419.
- Lee, H., y Romero, J. (2023) Climate change 2023: Synthesis report. Geneva, Switzerland: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
- Peixoto, R., Voolstra, C.R., Stein, L.Y., Hugenholtz, P., Salles, J.F., Amin, S.A., Häggblom, M., Gregory, A., Makhalanyane, T.P., Wang, F., Agbodjato, N.A., Wang, Y., Jiao, N., Lennon, J.T., Ventosa, A., Bavoil, P.M.,Miller, V., y Gilbert, J.A (2025). Microbial solutions must be deployed against climate catastrophe. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 23, 1-2
- Tiedje, J.M., Bruns M.A., Casadevall, A., Criddle, C.S., Eloe-Fadrosh, E., Karl, D.M., Nguyen, N.K., y Zhou, J. (2022).Microbes and Climate Change: a Research Prospectus for the Future. MBio, 13(3) 13:e00800-22.
- Verstraete, W., Yanuka‐Golub, K., Driesen, N., y De Vrieze, J. (2022). Engineering microbial technologies for environmental sustainability: choices to make. Microbial Biotechnology, 15(1), 215-227.
14. Filosfera: los guardianes microscópicos de las hojas
- Ling, M., Marshall, I. P., Rosati, B., Schreiber, L., Boesen, T., Finster, K., & Šantl-Temkiv, T. (2021). Properties relevant to atmospheric dispersal of the ice-nucleation active Pseudomonas syringae strain R10. 79 isolated from rain water. Aerobiologia, 37, 225-241.
- Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico (MITECO). (2023). Índice de área foliar. Gobierno de España.
- Muyshondt, B. (2023). An ecological perspective on phyllosphere bacterial communities in urban environments (Doctoral dissertation, University of Antwerp).
- Rastogi, G., Coaker, G. L., & Leveau, J. H. (2013). New insights into the structure and function of phyllosphere microbiota through high-throughput molecular approaches. FEMS microbiology letters, 348(1), 1-10.
- Remus‐Emsermann, M. N., & Schlechter, R. O. (2018). Phyllosphere microbiology: at the interface between microbial individuals and the plant host. New Phytologist, 218(4), 1327-1333.
- Wuyts, K., Smets, W., Lebeer, S., & Samson, R. (2020). Green infrastructure and atmospheric pollution shape diversity and composition of phyllosphere bacterial communities in an urban landscape. FEMS microbiology ecology, 96(1), fiz173.
15. Biodiversidad de microorganismos en cuevas visitables
- Fernandez-Cortes, A., Cuezva, S., Alvarez-Gallego, M., Garcia-Anton, E., Pla, C., Benavente, D., Jurado, V., Saiz-Jimenez, C., Sanchez-Moral, S. 2015. Subterranean atmospheres may act as daily methane sink. Nature Communications 6, 7003. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8003.
- Gonzalez-Pimentel, J.L., Dominguez-Moñino, I., Jurado, V., Laiz, L., Caldeira, A.T., Saiz-Jimenez, C. 2022. The rare actinobacterium Crossiella is a potential source of new bioactive compounds with activity against bacteria and fungi. Microorganisms 10, 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081575.
- Martin-Pozas, T., S. Cuezva, A. Fernandez-Cortes, J.C. Cañaveras, D. Benavente, V. Jurado, C. Saiz-Jimenez, I. Janssens, N. Seijas, S. Sanchez-Moral. 2022. Role of subterranean microbiota in the carbon cycle and greenhouse gas dynamics. Science of the Total Environment. 831, 154921. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154921
- Martin-Sanchez, P.M., Nováková, A., Bastian, F., Alabouvette, C., Saiz-Jimenez, C. 2012. Two new species of the genus Ochroconis, lascauxensis and O. anomala isolated from black stains in Lascaux Cave, France. Fungal Biology 116, 574-589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2012.02.006.
- Martin-Sanchez, P.M., Nováková, A., Bastian, F., Alabouvette, C., Saiz-Jimenez, C. 2012. Use of biocides for the control of fungal outbreaks in subterranean environments: The case of the Lascaux Cave in France. Environmental Science and Technology 46, 3762-3770. https://doi.org/dx.doi.org/10.1021/es2040625.
- Saiz-Jimenez, C., Cuezva, S., Jurado, V., Fernandez-Cortes, A., Porca, E., Benavente, D., Cañaveras, J.C., Sanchez-Moral, S. 2011. Paleolithic art in peril: Policy and science collide at Altamira Cave. Science 334, 42-43. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1206788.
- Saiz-Jimenez, C. 2022. Journey into darkness: microbes living in caves and mines. Frontiers for Young Minds, 10, 739199. https://doi.org/10.3389/frym.2022.739199.
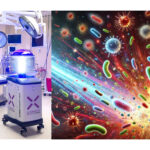
16. Xenex, la tecnología ‘no-touch’ de luz UV-C pulsada al servicio de los hospitales en la lucha contra las enfermedades nosocomiales
- Al-Tawfiq, J. A., & Tambyah, P. A. (2014). Healthcare associated infections (HAI) perspectives. Journal of infection and public health, 7(4), 339-344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2014.04.003
- Ananda, T., Modi, A., Chakraborty, I., Managuli, V., Mukhopadhyay, C., and Mazumder, N. (2022). Nosocomial infections and role of nanotechnology. , 9(2), 51. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9020051
- Anderson, J. G., Rowan, N. J., MacGregor, S. J., Fouracre, R. A., & Farish, O. (2000). Inactivation of food-borne enteropathogenic bacteria and spoilage fungi using pulsed-light. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 28(1), 83-88. https://doi.org/10.1109/27.842870
- Astrid, F., Beata, Z., Julia, E., Elisabeth, P., and Magda, D.E. (2021). The use of a UV-C disinfection robot in the routine cleaning process: a field study in an Academic hospital. Resist. Infect. Control, 10(1), 84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13756-021-00945-4
- Barg, N. L. (1993). Environmental contamination with Staphylococcus aureus and outbreaks: the cause or the effect?. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, 14(7), 367-368. https://doi.org/10.1086/646763
- Boyce, J. M. (2007). Environmental contamination makes an important contribution to hospital infection. Journal of hospital infection, 65, 50-54. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0195-6701(07)60015-2
- Boyce, J. M., Havill, N. L., Dumigan, D. G., Golebiewski, M., Balogun, O., & Rizvani, R. (2009). Monitoring the effectiveness of hospital cleaning practices by use of an adenosine triphosphate bioluminescence assay. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, 30(7), 678-684. https://doi.org/10.1086/598243
- Boyce, J.M. (2016). Modern technologies for improving cleaning and disinfection of environmental surfaces in hospitals. Resist. Infect. Control, 5, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13756-016-0111-x
- Buhr, T. L., Borgers-Klonkowski, E., Gutting, B. W., Hammer, E. E., Hamilton, S. M., Huhman, B. M., … & Young, A. A. (2022). Ultraviolet dosage and decontamination efficacy were widely variable across 14 UV devices after testing a dried enveloped ribonucleic acid virus surrogate for SARS-CoV-2. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 10, 875817. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.875817
- Bures, S., Fishbain, J. T., Uyehara, C. F., Parker, J. M., & Berg, B. W. (2000). Computer keyboards and faucet handles as reservoirs of nosocomial pathogens in the intensive care unit. American journal of infection control, 28(6), 465-471. https://doi.org/10.1067/mic.2000.107267
- Casini, B., Tuvo, B., Cristina, M.L., Spagnolo, A.M., Totaro, M., Baggiani, A., and Privitera, G.P. (2019). Evaluation of an ultraviolet C (UVC) light-emitting device for disinfection of high touch surfaces in hospital critical areas. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 16(19), 3572. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193572
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2014). CDC/NHSN surveillance definitions for specific types of infections. IOP Publishing CDC Website. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/pdfs/pscmanual/17pscnosinfdef_current.pdf
- Cheigh, C. I., Park, M. H., Chung, M. S., Shin, J. K., & Park, Y. S. (2012). Comparison of intense pulsed light-and ultraviolet (UVC)-induced cell damage in Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157: H7. Food Control, 25(2), 654-659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.11.032
- Commission Delegated Directive (EU) 2022/274-284. Commission Delegated Directive (EU) 2022/274 of 13 December 2021 amending, for the purposes of adapting to scientific and technical progress, Annex III to Directive 2011/65/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards an exemption for the use of mercury in cold cathode fluorescent lamps and external electrode fluorescent lamps for special purposes. http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir_del/2022/274/oj
- Cowen, A. E. (2001). The clinical risks of infection associated with endoscopy. Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 15(5), 321-331. https://doi.org/10.1155/2001/691584
- Dancer, S.J. (2009). The role of environmental cleaning in the control of hospital-acquired infection. Hosp. Infect., 73(4), 378-385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2009.03.030
- Derraik, J. G., Anderson, W. A., Connelly, E. A., & Anderson, Y. C. (2020). Rapid evidence summary on SARS-CoV-2 survivorship and disinfection, and a reusable PPE protocol using a double-hit process. MedRxiv, 2020-04. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.02.20051409
- Diffey, B. L. (1988). The risk of skin cancer from occupational exposure to ultraviolet radiation in hospitals. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 33(10), 1187. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/33/10/007
- Dippenaar, R., & Smith, J. (2018). Impact of pulsed xenon ultraviolet disinfection on surface contamination in a hospital facility’s expressed human milk feed preparation area. BMC infectious diseases, 18, 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-018-2997-9
- Directive, E. C. (2011). Directive 2011/65/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 8 June 2011, on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment (recast). Official Journal of the European Communities. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2011:174:0088:0110:en:PDF
- Duarte, I., Rotter, A., Malvestiti, A., & Silva, M. (2009). The role of glass as a barrier against the transmission of ultraviolet radiation: an experimental study. Photodermatology, photoimmunology & photomedicine, 25(4), 181-184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0781.2009.00434.x
- El-Haddad, L., Ghantoji, S. S., Stibich, M., Fleming, J. B., Segal, C., Ware, K. M., & Chemaly, R. F. (2017). Evaluation of a pulsed xenon ultraviolet disinfection system to decrease bacterial contamination in operating rooms. BMC Infectious Diseases, 17, 1-5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2792-z
- Fornwalt, L., Ennis, D., and Stibich, M. (2016). Influence of a total joint infection control bundle on surgical site infection rates. J. Infect. Control, 44(2), 239-241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2015.09.010
- Geroulanos, S., Hell, K., & Largiadèr, F. (1991). Infecciones Postoperatorias. Ed. Roche Ltd., Basel, Switzerland. ISBN: 3-907946-54-5, ISBN: 84-86917-46-8.
- Getchell-White, S. I., Donowitz, L. G., & Groschel, D. H. (1989). The inanimate environment of an intensive care unit as a potential source of nosocomial bacteria: evidence for long survival of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, 10(9), 402-407. https://doi.org/10.1086/646061
- Ghantoji, S. S., Stibich, M., Stachowiak, J., Cantu, S., Adachi, J. A., Raad, I. I., & Chemaly, R. F. (2015). Non-inferiority of pulsed xenon UV light versus bleach for reducing environmental Clostridium difficile contamination on high-touch surfaces in Clostridium difficile infection isolation rooms. Journal of medical microbiology, 64(2), 191-194. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.000004
- Han, A., Han, E., and Han Hv, E. (2011). Directive 2011/65/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 8 June 2011 on the Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment. Harting: Espelkamp, Germany. https://www.harting.com/sites/default/files/2017-09/RoHS_EL_several_articles-EN.pdf
- Haas, J. P., Menz, J., Dusza, S., & Montecalvo, M. A. (2014). Implementation and impact of ultraviolet environmental disinfection in an acute care setting. American journal of infection control, 42(6), 586-590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2013.12.013
- Hassan, K.A., Aftab, A., and Riffat, M. (2015). Nosocomial infections and their control strategies. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed., 505-509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.05.001
- Hausemann, A., Grünewald, M., Otto, U., and Heudorf, U. (2018). Cleaning and disinfection of surfaces in hospitals. Improvement in quality of structure, process and outcome in the hospitals in Frankfurt/Main, Germany, in 2016 compared to 2014. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control, 13. https://doi.org/10.3205/dgkh000312
- Holland, J., Kingston, L., McCarthy, C., Armstrong, E., O’Dwyer, P., Merz, F., & McConnell, M. (2021). Service robots in the healthcare sector. Robotics, 10(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics10010047
- Huber, T. W., Brackens, E., Chatterjee, P., Villamaria, F. C., Sisco, L. E., Williams, M. D., … & Jinadatha, C. (2020). Efficacy of pulsed-xenon ultraviolet light on reduction of Mycobacterium fortuitum. SAGE Open Medicine, 8, 2050312120962372. https://doi.org/10.1177/20503121209623
- Huttner, A., Harbarth, S., Carlet, J., Cosgrove, S., Goossens, H., Holmes, A., & World Healthcare-Associated Infections Forum participants. (2013). Antimicrobial resistance: a global view from the 2013 World Healthcare-Associated Infections Forum. Antimicrobial resistance and infection control, 2, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-2994-2-31
- Ibrahim, M. A., MacAdam, J., Autin, O., & Jefferson, B. (2014). Evaluating the impact of LED bulb development on the economic viability of ultraviolet technology for disinfection. Environmental technology, 35(4), 400-406. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2013.829858
- Jinadatha, C., Quezada, R., Huber, T. W., Williams, J. B., Zeber, J. E., & Copeland, L. A. (2014). Evaluation of a pulsed-xenon ultraviolet room disinfection device for impact on contamination levels of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. BMC infectious diseases, 14, 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-14-187
- Jinadatha, C., Simmons, S., Dale, C., Ganachari-Mallappa, N., Villamaria, F. C., Goulding, N., … & Stibich, M. (2015). Disinfecting personal protective equipment with pulsed xenon ultraviolet as a risk mitigation strategy for health care workers. American journal of infection control, 43(4), 412-414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2015.01.013
- Joshi, M., Kaur, S., Kaur, H.P., and Mishra, T. (2019). Nosocomial infection: source and prevention. J Pharm. Sci. Res., 10(4), 1613-1624. http://dx.doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.10(4).1613-24
- Khan, H. A., Ahmad, A., & Mehboob, R. (2015). Nosocomial infections and their control strategies. Asian pacific journal of tropical biomedicine, 5(7), 509-514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.05.001
- Khan, H. A., Baig, F. K., & Mehboob, R. (2017). Nosocomial infections: Epidemiology, prevention, control and surveillance. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 7(5), 478-482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2017.01.019
- Kiyosawa, K., Tanaka, M., Matsunaga, T., Nikaido, O., & Yamamoto, K. (2001). Amplified UvrA protein can ameliorate the ultraviolet sensitivity of an Escherichia coli recA mutant. Mutation Research/DNA Repair, 487(3-4), 149-156. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8777(01)00114-8
- Legesse Laloto, T., Hiko Gemeda, D., and Abdella, S.H. (2017). Incidence and predictors of surgical site infection in Ethiopia: prospective cohort. BMC Infect. Dis., 17, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-016-2167-x
- Levin, J., Riley, L. S., Parrish, C., English, D., & Ahn, S. (2013). The effect of portable pulsed xenon ultraviolet light after terminal cleaning on hospital-associated Clostridium difficile infection in a community hospital. American journal of infection control, 41(8), 746-748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2013.02.010
- Lipatov, E.I., Sosnin, E.A., & Avdeev, S.M. (2015). The inactivation of eggs of helminthes under the action of narrowband ultraviolet radiation of excilamps. In International Conference on Atomic and Molecular Pulsed Lasers XII (Vol. 9810, pp. 225-230). SPIE. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2228995
- Kollef, M.H., Torres, A., Shorr, A.F., Martin-Loeches, I., and Micek, S.T. (2021). Nosocomial infection. Care Med., 49(2), 169-187. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000004783
- Maclayton, D. O., & Hall, R. G. (2007). Infectious Diseases: Pharmacologic Treatment Options for Nosocomial Pneumonia Involving Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 41(2), 235-244. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1H414
- Mangram, A.J., Horan, T.C., Pearson, M.L., Silver, L.C., Jarvis, W.R., and Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. (1999). Guideline for prevention of surgical site infection, 1999. Control Hosp. Epidemiol., 20(4), 247-280. https://doi.org/10.1086/501620
- Marra, A.R., Schweizer, M.L., and Edmond, M.B. (2018). No-touch disinfection methods to decrease multidrug-resistant organism infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Control Hosp. Epidemiol., 39(1), 20-31. https://doi.org/10.1017/ice.2017.226
- Maslo, C., du Plooy, M., & Coetzee, J. (2019). The efficacy of pulsed-xenon ultraviolet light technology on Candida auris. BMC infectious diseases, 19, 1-3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-019-4137-6
- McDonald, K. F., Curry, R. D., Clevenger, T. E., Unklesbay, K., Eisenstark, A., Golden, J., & Morgan, R. D. (2000). A comparison of pulsed and continuous ultraviolet light sources for the decontamination of surfaces. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 28(5), 1581-1587. https://doi.org/10.1109/27.901237
- Mehta, I., Hsueh, H. Y., Taghipour, S., Li, W., & Saeedi, S. (2023). UV disinfection robots: a review. Robotics and autonomous systems, 161, 104332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.robot.2022.104332
- Mitchell, D. L., Jen, J., & Cleaver, J. E. (1992). Sequence specificity of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers in DNA treated with solar (ultraviolet B) radiation. Nucleic acids research, 20(2), 225-229. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/20.2.225
- Mohebbi, Z., Setoodeh, G., and Bagheri, S.H. (2018). Surgical site infection in the world and in Iran: Causes and outcomes. 2018. Available at: URL: https://www.omicsonline.org/proceedings/surgical-site-infection-in-the-world-and-in-iran-causes-and-outcomes-93074.html.
- Nagaraja, A., Visintainer, P., Haas, J. P., Menz, J., Wormser, G. P., & Montecalvo, M. A. (2015). Clostridium difficile infections before and during use of ultraviolet disinfection. American Journal of Infection Control, 43(9), 940-945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2015.05.003
- Nerandzic, M. M., Thota, P., Sankar, T., Jencson, A., Cadnum, J. L., Ray, A. J., … & Donskey, C. J. (2015). Evaluation of a pulsed xenon ultraviolet disinfection system for reduction of healthcare-associated pathogens in hospital rooms. Infection control & hospital epidemiology, 36(2), 192-197. https://doi.org/10.1017/ice.2014.36
- Noskin, G. A., Stosor, V., Cooper, I., & Peterson, L. R. (1995). Recovery of vancomycin-resistant enterococci on fingertips and environmental surfaces. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, 16(10), 577-581. https://doi.org/10.1086/647011
- Oguma, K., Katayama, H., & Ohgaki, S. (2001). Determination of pyrimidine dimmers in the chromosomal DNA of Escherichia coli during photoreactivation following inactivation by medium-pressure UV lamp. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 4630-4637. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.10.4630-4637.2001
- Oliveira, R.M.C., de Sousa, A.H.F., de Salvo, M.A., Petenate, A.J., Gushken, A.K.F., Ribas, E., Torelly, E.M.S., Silva, K.C.C.D., Bass, L.M., Tuma, P., Borem, P., Ue, L.Y., de Barros, C.G., and Vernal, S. (2024). Estimating the savings of a national project to prevent healthcare-associated infections in intensive care units. Hosp. Infect., 143, 8-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2023.10.001
- O’Neill, J. (2016). Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: final report and recommendations. THE REVIEW ON ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE. UK Government. https://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/160518_Final%20paper_with%20cover.pdf
- Otaki M, Okuda A, Tajima K, Iwasaki T, Kinoshita S, Ohgaki S (2003) Inactivation differences of microorganisms by low pressure UV and pulsed xenon lamps. BMC Infect Dis 3:1–10. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2003.0193
- Otter, J.A., Yezli, S., and French, G.L. (2011). The role played by contaminated surfaces in the transmission of nosocomial pathogens. Control Hosp. Epidemiol., 32(7), 687-699. https://doi.org/10.1086/660363
- Ratliff, K., Oudejans, L., Calfee, W., Abdel‐Hady, A., Monge, M., & Aslett, D. (2022). Evaluating the impact of ultraviolet C exposure conditions on coliphage MS2 inactivation on surfaces. Letters in applied microbiology, 75(4), 933-941. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13770
- Rowan, N. J., MacGregor, S. J., Anderson, J. G., Fouracre, R. A., McIlvaney, L., & Farish, O. (1999). Pulsed-light inactivation of food-related microorganisms. Applied and environmental microbiology, 65(3), 1312-1315. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.65.3.1312-1315.1999
- San Antonio Express-news. (2023, Sep 6). Xenex’s pathogen-zapping LightStrike robot gets FDA authorization for use in health care facilities [Press Release]. https://www.expressnews.com/business/article/xenex-lightstrike-robot-gets-fda-approval-use-18348580.php
- San Antonio Express-news. (2024, April 18). Morris Miller, CEO of Xenex, wants to invade U.S. hospitals with germ-killing robots [Press Release]. https://www.expressnews.com/sa-inc/article/xenex-morris-miller-hospitals-germ-killing-robots-19252506.php
- Schaefer, R., Grapperhaus, M., Schaefer, I., & Linden, K. (2007). Pulsed UV lamp performance and comparison with UV mercury lamps. Journal of Environmental Engineering and Science, 6(3), 303-310. https://doi.org/10.1139/s06-068
- Septimus, E.J., and Moody, J. (2016). Prevention of device-related healthcare-associated infections. F1000Research, 5. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.7493.1
- Simmons, S., Dale Jr, C., Holt, J., Passey, D.G., and Stibich, M. (2018). Environmental effectiveness of pulsed-xenon light in the operating room. J. Infect. Control, 46(9), 1003-1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2018.02.027
- Simmons, S. E., Carrion, R., Alfson, K. J., Staples, H. M., Jinadatha, C., Jarvis, W. R., … & Stibich, M. A. (2021). Deactivation of SARS-CoV-2 with pulsed-xenon ultraviolet light: Implications for environmental COVID-19 control. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, 42(2), 127-130. https://doi.org/10.1017/ice.2020.399
- Stibich, M., Simmons, S., and Passey, D. (2020). 10 Years of Pulsed-Xenon Ultraviolet Disinfection. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, 41(S1), s438-s438. https://doi.org/10.1017/ice.2020.1104
- Stibich, M., and Stachowiak, J. (2016). The microbiological impact of pulsed xenon ultraviolet disinfection on resistant bacteria, bacterial spore and fungi and viruses. Southern African Journal of Infectious Diseases, 31(1), 12-15. https://doi.org/10.4102/sajid.v31i1.103
- Stibich, M., Stachowiak, J., Tanner, B., Berkheiser, M., Moore, L., Raad, I., & Chemaly, R. F. (2011). Evaluation of a pulsed-xenon ultraviolet room disinfection device for impact on hospital operations and microbial reduction. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, 32(3), 286-288. https://doi.org/10.1086/658329
- Taherpour, N., Mehrabi, Y., Seifi, A., Eshrati, B., and Hashemi Nazari, S.S. (2021). Epidemiologic characteristics of orthopedic surgical site infections and under-reporting estimation of registries using capture-recapture analysis. BMC Infect. Dis., 21, 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-020-05687-z
- UNEP, United Nations Environment Programme. 2019. Minamata Convention On Mercury. https://minamataconvention.org/
- Vieira, G.D.D., Mendonça, H. R., Alves, T.D.C., Araújo, D.F.D.O., Silveira Filho, M.L.D., Freitas, A.P.D.S.R.D., et al. (2015). Survey of infection in orthopedic postoperative and their causative agents: a prospective study. Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira, 61, 341-346. https://doi.org/10.1590/1806-9282.61.04.341
- Villacís, J.E., Lopez, M., Passey, D., Santillán, M.H., Verdezoto, G., Trujillo, F., Paredes, G., Alarcón, C., Horvath, R., and Stibich, M. (2019). Efficacy of pulsed-xenon ultraviolet light for disinfection of high-touch surfaces in an Ecuadorian hospital. BMC Infect. Dis., 19, 575. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-019-4200-3
- Weber, D. J., Anderson, D., & Rutala, W. A. (2013). The role of the surface environment in healthcare-associated infections. Current opinion in infectious diseases, 26(4), 338-344. https://doi.org/10.1097/QCO.0b013e3283630f04
- Weber, D. J., and Rutala, W.A. (2013). Understanding and preventing transmission of healthcare-associated pathogens due to the contaminated hospital environment. Control Hosp. Epidemiol., 34(5), 449-452. https://doi.org/10.1086/670223
- World Health Organization. (2016). Guidelines on core components of infection prevention and control programmes at the national and acute health care facility level. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549929